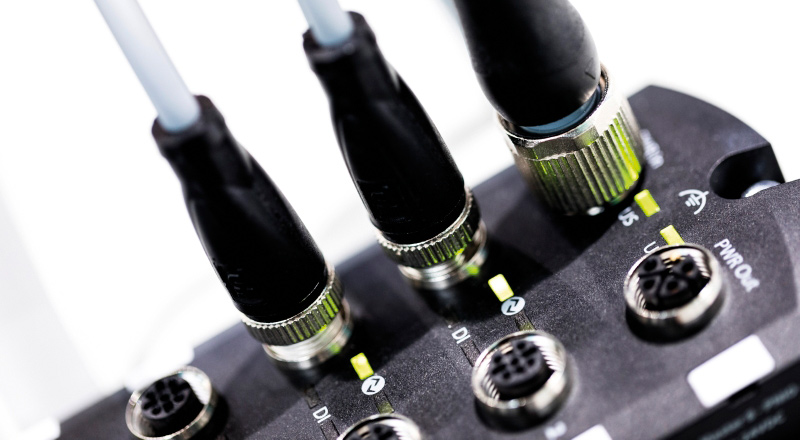
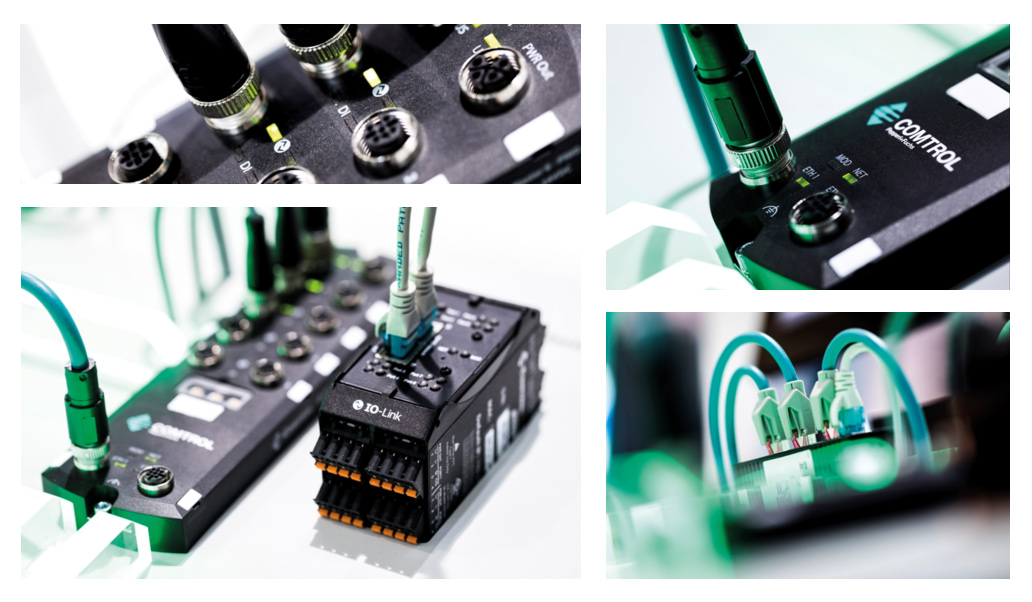
Technologies
Learn more about intelligent communication technologies such as IO-Link, RFID, or Ethernet-APL, which enable transparent and digitized processes in your plant. These key technologies for setting up IIoT networks ensure reliable data transmission from the field level to the controller, to software systems, and into the cloud. In addition, Pepperl+Fuchs offers an IoT system based on an ultrasonic sensor using LoRaWAN® technology, which autonomously transmits data over a range of several kilometers.

Technologies
Learn more about intelligent communication technologies such as IO-Link, RFID, or Ethernet-APL, which enable transparent and digitized processes in your plant. These key technologies for setting up IIoT networks ensure reliable data transmission from the field level to the controller, to software systems, and into the cloud. In addition, Pepperl+Fuchs offers an IoT system based on an ultrasonic sensor using LoRaWAN® technology, which autonomously transmits data over a range of several kilometers.

How RFID with IO-Link Eases Machine Access
The use of RFID for machine access control and operation is nothing new. Depending on the application, different frequency ranges are used, either LF, HF, or UHF. Recently, there has been a trend that HF read/write heads with IO-Link are increasingly being used for precisely these applications. In this blog article we take a closer look at this topic and show you possible use cases.
RFID Meets AGV—Three Examples of Practical Applications
Used intelligently, RFID can perform numerous tasks on the automated guided vehicles (AGV)—we present three possible variants in this blog article.
IO-Link as a Retrofit Solution for Legacy Systems
In this article, you will learn more about the advantages of intelligent communication technology and how you can modernize existing systems with IO-Link masters from Pepperl+Fuchs.
5 Reasons for the Industrial Use of LoRaWAN Technology
As Industry 4.0 grows, interest in radio-based sensors is also increasing. LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is one technology that is becoming more and more popular in this context and is attracting the attention of industrial companies.
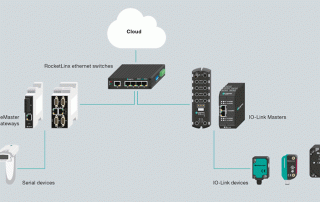
Industrial Internet of Things with MQTT and IO-Link Technology
Do you wonder if switching to MQTT-compliant devices could improve your application? Here is what you must know to build an IIoT-ready system.
IO-Link Masters Make Factories Smarter
Industry 4.0 applications require sensors that are able to communicate with PLCs and higher-level SCADA or cloud systems. Pepperl+Fuchs IO-Link masters with MultiLink™ technology enable smarter factories.
4 Ways to Digitalize Your Factory
Digitalization can be daunting. But with the right technologies, you can prepare your factory for Industry 4.0 and build IIoT networks.
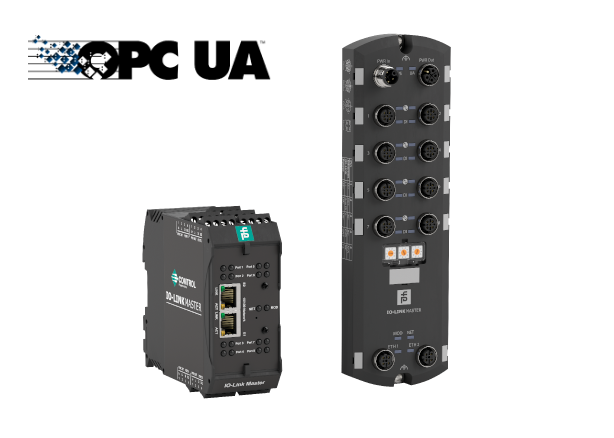
Four Scenarios for Using IO-Link Masters with OPC UA Interface
IO-Link master with OPC UA interface create a uniform basis for continuous information exchange from the field to the cloud. In this article, we will show you what applications are possible with the open data exchange standard.
8 Advantages of IO-Link
The IO-Link communication protocol is a standard interface and offers many advantages. We have picked up eight advantages of IO-Link.
Five Reasons to Use Industrial RFID in Your Meat Processing Plant
If you want to establish internal food traceability in a meat processing plant, you face a number of challenges: Diverse processes, harsh environmental conditions, hygiene requirements and different transport routes demand a flexible and at the same time reliable technology. Industrial RFID offers a solution for this and also, depending on the application, other additional benefits.
Ten Application Examples for RFID in Industrial Automation
RFID is one of the most versatile technologies in industrial automation. Whatever industry you may be thinking of—it is highly likely that RFID will be used there. We have compiled ten RFID applications that give you ideas for possible applications and demonstrate the advantages of this identification technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on RFID (Part 4): RFID Tags
RFID tags carry information on a certain object or transport container. The size of an RFID tag can vary from the dimensions of a match head to a brick. While some tags are used simply as an attachable ID for an object, others carry a variety of different attributes relating to the object.
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive regular news and interesting facts from the world of automation.