How RFID with IO-Link Eases Machine Access
Content of This Article
How RFID with IO-Link Eases Machine Access
The use of RFID for machine access control and operation is nothing new. Depending on the application, different frequency ranges are used, either LF, HF, or UHF. Recently, there has been a trend that HF read/write heads with IO-Link are increasingly being used for precisely these applications. As always, the goal is to ensure only authorized personnel operate machinery. Also valued is the ability to retrieve an operation log and how each worker parameterizes the machines.
Users who were previously of the opinion that RFID was somehow too complicated have quickly changed their view in practice. In this blog article we take a closer look at the topic and show you possible use cases.
How Does RFID with IO-Link Work?
The operation of HF read/write heads with IO-Link is simple and intuitive. Starting in “Easy Mode”, the heads instantly start looking for an RFID tag to read. A user-friendly web interface allows easy parameterization and setting changes.
An RFID card, i.e., an RFID transponder in credit card format, is a great solution for machine access applications. To operate a machine, a potential user waves its card over the RFID reader. The data is checked against a truth table in a PLC to make sure the user is allowed to operate the machine. Using RFID read/write heads with IO-Link, login data could be sent to a database to keep track of who logs in, and when.

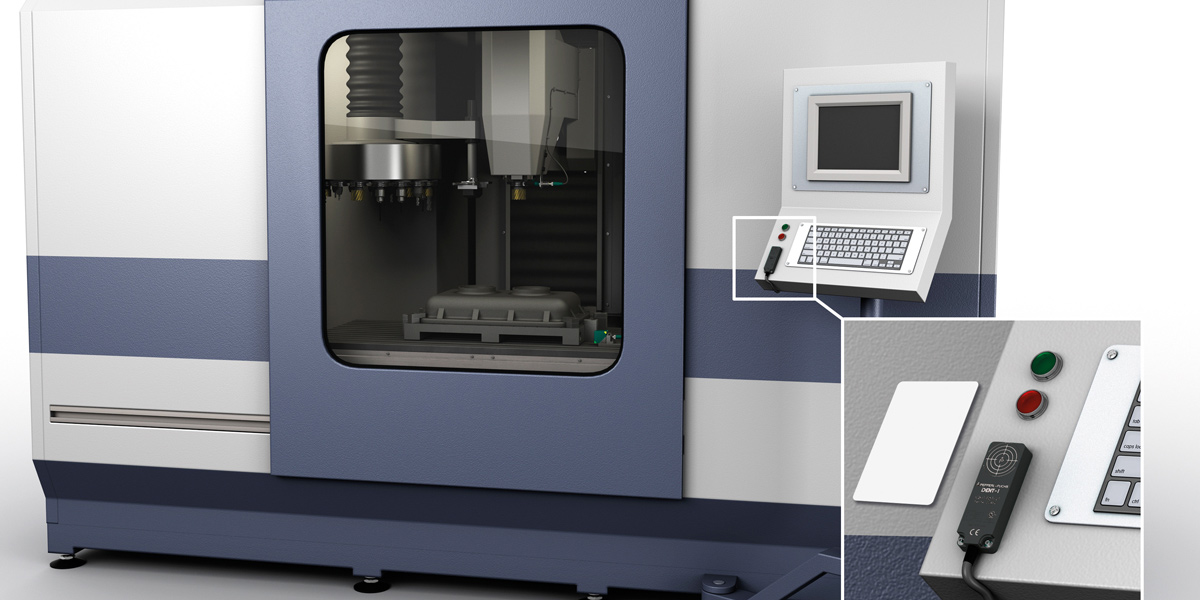
Machine operators only have to hold their RFID transponder over the RFID reader and authorization takes place automatically and in real time. Pictured here is the Pepperl+Fuchs IQT1-F61-IO read/write station with IO-Link.
For the connection of IO-Link devices you need an IO-Link master. Up to eight HF read/write heads with IO-Link can be connected per IO-Link master. This makes it easy and affordable to set up multiple reading points on the machine to enable the tiered approval of machine operation. If the software or machine to be accessed has an appropriate rights and roles concept, operators, service personnel, and administrators could each have their own read point.
Three Examples for Machine Access Applications Using RFID with IO-Link
Automatic Ball Bearing Sorting Machines
Only authorized personnel are allowed to operate the machine that sorts and delivers a specific number of balls into each ball bearing. If the wrong amount of balls are added to a bearing, the bearing could fail in a dangerous way.
Transformer Production

Also in transformer production, only authorized personnel should operate the cranes which lift large parts and assembled pieces during production. An operator without the necessary skills could cause injuries to himself or others, halting the production process, and damage valued assets.
Crane Lifters

Huge cranes that lift cargo containers should only be operated by trained personnel. If a mistake happens, such as using the wrong size lifting apparatus, an electronic operation log is very useful. Mistakes can be addressed more easily and prevented in the future.
Want to Get Started?
RFID in combination with IO-Link holds great potential for increasing efficiency in machine access. If you would also like to implement RFID for your application, we recommend you take a look at our portfolio of RFID components. Our experts look forward to your inquiry.
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive regular news and interesting facts from the world of automation.
