Knowledge Base
Pepperl+Fuchs offers a large portfolio of devices, solutions, and technologies for a wide variety of industrial applications and explosion protection. But have you ever wondered what is actually behind certain technologies or how individual products vary from one another? In the Pepperl+Fuchs knowledge base section, we answer general questions and provide assistance on our technologies and products.

Knowledge Base
Pepperl+Fuchs offers a large portfolio of devices, solutions, and technologies for a wide variety of industrial applications and explosion protection. But have you ever wondered what is actually behind certain technologies or how individual products vary from one another? In the Pepperl+Fuchs knowledge base section, we answer general questions and provide assistance on our technologies and products.

How is a type code from Pepperl+Fuchs structured?
How Is a Type Code from Pepperl+Fuchs Structured? Our product portfolio of thousands of sensors includes: inductive, capacitive, magnetic field and ultrasonic sensors as well as sensors for special applications. To help you find the right sensor for your applications, we explain below how a type code from Pepperl+Fuchs is composed. Type codes from Pepperl+Fuchs are composed of three categories for the above sensors: In the first category, a distinction is made between functional principles (sensor type), application-specific features (type of use), installation situation (flush/non-flush) and the sensing distance. In the second category, a distinction is made [...]
What Are the Differences between the K-System and the H-System?
Pepperl+Fuchs offers two extensive product families for safely transmitting signals between the field and control levels: the K-System and the H-System. Get to know the differences between and benefits of these two systems, and explains for whom each system is most suitable.
What Are Industrial Thin Clients? Part 2/2—The Benefits
Over the past decade, thin clients have become more and more popular in process automation and industrial applications. The trend toward virtualization makes thin clients an especially cost-effective solution as they allow users to access applications and information stored on centralized systems such as servers. Learn more about the benefits of thin clients in this blog post.
What Are Industrial Thin Clients? Part 1/2—How It Works
Explosive atmospheres, harsh environments, extreme temperatures—the process industry places unique demands on the people and technology working in the sector. This also applies to thin clients, as they are known in office applications. Unlike traditional PCs, thin clients run applications on remote servers rather than on the local hardware, and only transmit image information and user inputs over the network.
Ultrasonic Sensor FAQ: Synchronization and Common Mode
In this blog article, we explain what needs to be considered when installing multiple ultrasonic sensors and how to prevent potential switching faults by synchronization.
Ultrasonic Sensor FAQ: Mounting Tips
To avoid incorrect measurement results of your ultrasonic sensor in the plant, we answer some frequently asked customer questions regarding mounting.
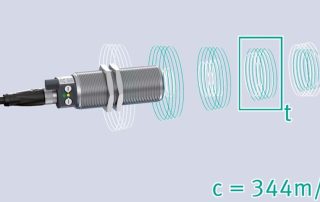
Ultrasonic Sensor FAQ: Detection Range and Accuracy
To choose the right ultrasonic sensor for a particular application, it is necessary to determine which factors affect the detection range and accuracy of ultrasonic sensors and how incorrect measurements can be corrected.
Ultrasonic Sensor FAQ: External Influences on Sensor Operation
How do temperature, rain, and other external factors influence the performance of ultrasonic sensors? Read the blog article below to find out how ultrasonic sensors from Pepperl+Fuchs handle extreme conditions.
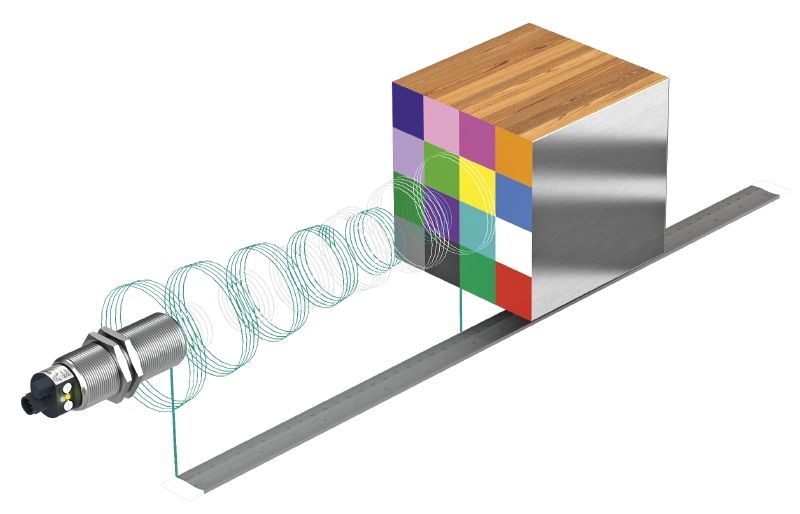
Ultrasonic Sensor FAQ: Differences between Diffuse Mode Sensor, Retroreflective Sensor, and Thru-Beam Sensor
Different operating modes can be achieved with ultrasonic sensors with switching output by appropriate construction and configuration. Learn more in this blog article about how diffuse mode sensors, retroreflective sensors, and ultrasonic thru-beam sensors work.
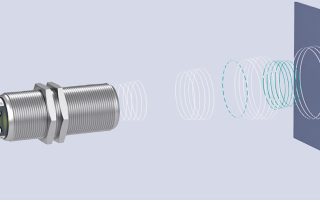
Ultrasonic Sensor FAQ: Ultrasonic Technology and Functions at a Glance
This blog article introduces the ultrasonic technology and its function principles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on RFID (Part 1)
RFID stands for “radio frequency identification” and refers to technologies that use radio waves to identify objects or people automatically. RFID makes use of the so-called “air interface,” transmitting electromagnetic waves through the air. Typically, a serial number or other product- /object-related information (“identifier”) is stored on a microchip. This chip is attached to an antenna that enables the chip to transfer the information needed for identification to a reading device.
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive regular news and interesting facts from the world of automation.