We are pleased to welcome you to our blog. Here you will find useful information, applications, and guidance on the topics of automation, industrial sensors, and explosion protection.

Welcome to our blog. Here you will find current articles on the topics of industrial automation and sensor technology.
Inclination Sensors: Pointing Solar Power in the Right Direction
Solar power is one of the most important answers to the question of renewable energy. Pepperl+Fuchs inclination sensors can make solar power plants even more productive.
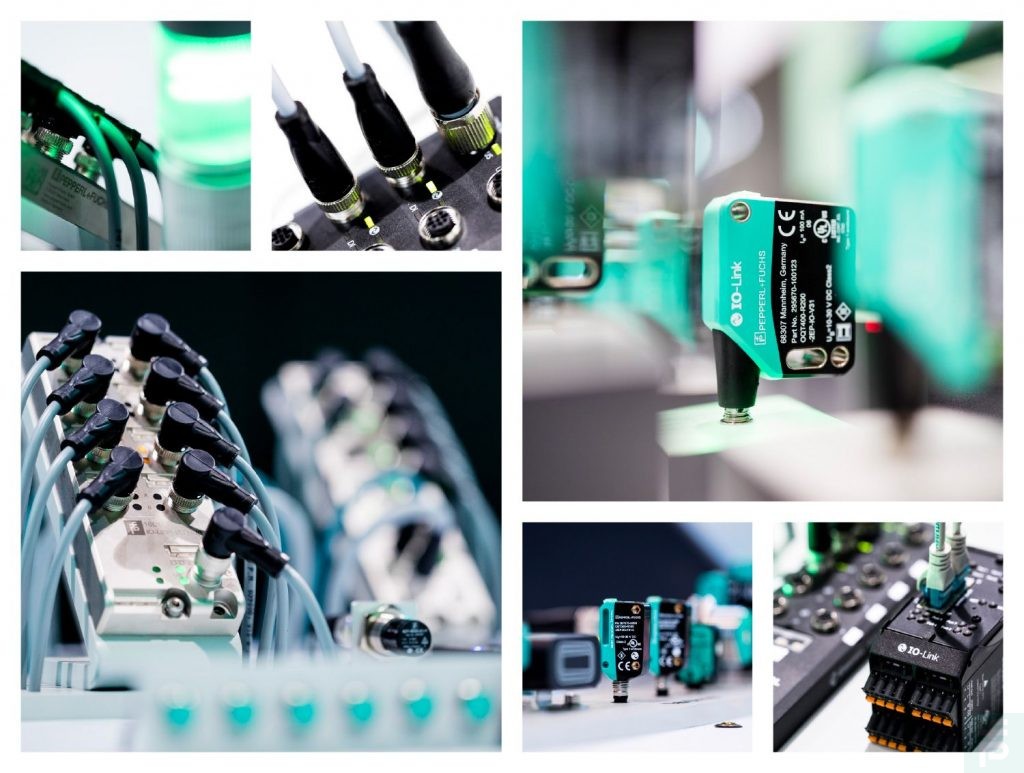
8 Advantages of IO-Link
The IO-Link communication protocol is a standard interface and offers many advantages. We have picked up eight advantages of IO-Link.
Can Ultrasonic Double Sheet Sensors Be Used for Label Detection?
Ultrasonic double sheet sensors help ensure continuous, error-free processes in a range of industrial applications. They are used to prevent more than one layer of material from being fed into a machine. The same technology behind double sheet detection can also be applied to label detection applications.
How is a type code from Pepperl+Fuchs structured?
How Is a Type Code from Pepperl+Fuchs Structured? Our product portfolio of thousands of sensors includes: inductive, capacitive, magnetic field and ultrasonic sensors as well as sensors for special applications. To help you find the right sensor for your applications, we explain below how a type code from Pepperl+Fuchs is composed. Type codes from Pepperl+Fuchs are composed of three categories for the above sensors: In the first category, a distinction is made between functional principles (sensor type), application-specific features (type of use), installation situation (flush/non-flush) and the sensing distance. In the second category, a distinction is made [...]
What Are the Differences between the K-System and the H-System?
Pepperl+Fuchs offers two extensive product families for safely transmitting signals between the field and control levels: the K-System and the H-System. Get to know the differences between and benefits of these two systems, and explains for whom each system is most suitable.
What Are Industrial Thin Clients? Part 2/2—The Benefits
Over the past decade, thin clients have become more and more popular in process automation and industrial applications. The trend toward virtualization makes thin clients an especially cost-effective solution as they allow users to access applications and information stored on centralized systems such as servers. Learn more about the benefits of thin clients in this blog post.
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive regularly news and interesting information around the world of automation.