PS1000 Industrial Power Supplies in Redundant Architectures up to Zone 2/Div. 2
Content of This Article
PS1000 Industrial Power Supplies in Redundant Architectures up to Zone 2/Div. 2
Industrial power supplies of the PS1000 series are used everywhere in automation technology where high system availability, redundancy and economic efficiency are required. In the control cabinet and in field boxes in all industrial applications and process systems, they ensure an efficient and reliable power supply from 5 Amps to 40 Amps, for 12 VDC, 24 VDC or 48 VDC output. The PS1000 devices have ATEX, IECEx, and EAC approvals and are also certified for the North American market, allowing them to be used up to Zone 2/Div.2.
The PS1000 series includes 1- and 3-phase power supplies as well as modules with built-in redundancy and redundancy modules. In this blog article, we take a closer look at the advantages and functionalities of these modules and support you in setting up your redundant power supply.
High efficiency, Reduced Energy Costs
The PS1000 power supplies are characterized by absolute reliability and a particularly high degree of efficiency of approx. 95 %. The high degree of efficiency not only reduces the use of hardware, since the devices have hardly any losses in terms of the power fed in, but also considerably minimizes the effort required for cooling in the control cabinet. In this way, you also reduce your energy costs.
Since the PS1000 power supplies are the smallest and lightest devices in their class, they only take up little space. With their compact design, the modules can be easily mounted on DIN rails and can be used in ambient temperatures of up to +70 °C. The cable length can also be compensated in the application, since the output voltage is adjustable.
In the control cabinet, the modules can be easily combined with other Pepperl+Fuchs DIN rail mounted products such as intrinsic safety barriers, signal conditioners and surge protection modules.
When the input voltage is applied, the inrush current is actively limited and networks and other devices are therefore protected. The “Peak Output Power” function also enables heavy loads such as motors and electronic devices to be switched on.
Redundant Power Supplies
Power supply redundancy is an important means to increase system reliability. Industrial process facilities rely tremendously on bulk power supplies because they not only power the control system architecture, but can also power the process measurement instrumentation. Applications that are critical and run continuously cannot afford to be shut down due to a power supply failure. A single failure could have a catastrophic effect that equates to a tremendous amount of lost revenue for every minute the process is down.
This need for system integrity and guaranteed performance in these demanding conditions necessitates power redundancy. N+1 and 1+1 are two reliable redundancy methods that guarantee system functionality will continue even during a power supply failure, resulting in very low MTTR (Mean Time to Repair).
N+1 and 1+1 Topologies Explained
The PS1000 series offers economical reliability and redundancy for your power supplies. The devices can be used redundantly in both an N+1 and a 1+1 topology. With an N+1 redundant configuration, multiple components (N) have at least one independent backup component (+1) to ensure system functionality continues in the event of a power failure. All modules within the configuration share the load. If a module in the system fails, the functioning modules can continue to share the load without compromising the integrity of the system. 1+1 configurations (also referred to as N+N) provide redundancy with two power modules of the same power, coupled by a MOSFET, working together to supply the same load. The redundancy function utilizes MOSFETs instead of diodes for the decoupling of the two input channels, which reduces the heat generation and the voltage drop between input and output.
Utilizing Redundancy with the New PS1000 Series Power Supplies
The PS1000 series can be used in redundant topologies either by using an external redundancy module PS1000 – **. RM that has a decoupling MOSFET on the input, which allows connection of two power supplies for 1+1 redundancy, or by using PS1000 – **. R power supplies with decoupling MOSFET built into the power module for applications with limited space in the control cabinet.
For applications requiring less than 40 A, 1+1 redundancy is an economical solution when a redundant power system is required, whereas N+1 is used for more critical applications.
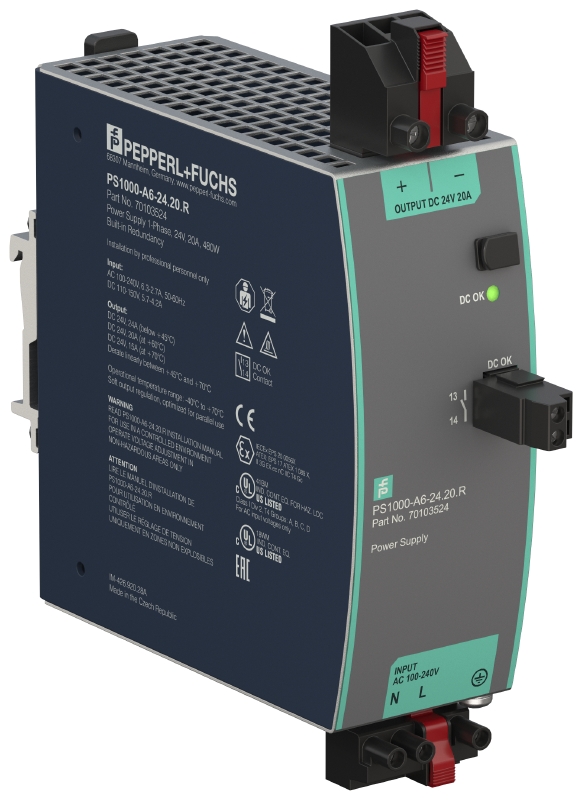



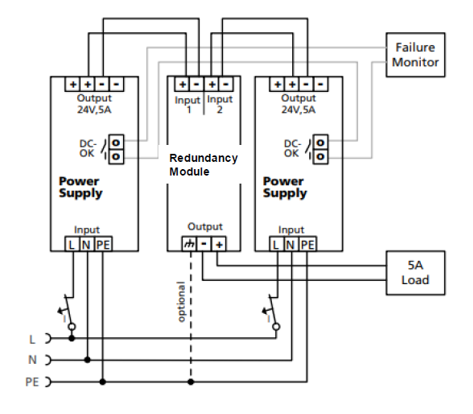
Figure 1 – PS1000-**.RM – External redundancy module for a 5 A load in a 1+1 configuration
N+1 redundancy can also be achieved using multiple external redundancy modules:
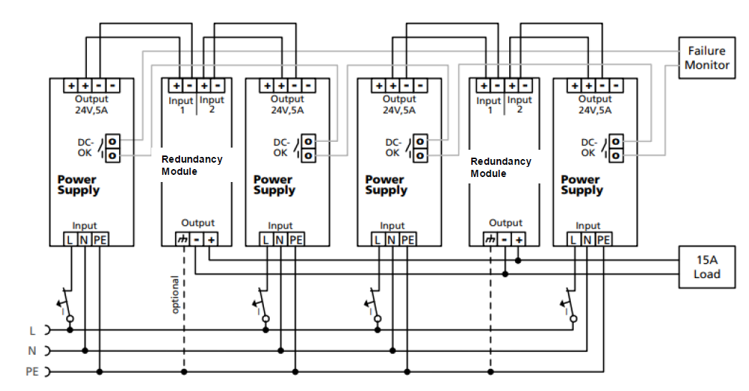
Figure 2 – PS1000-**.RM – External redundancy modules for 15 A load in N+1 configuration
N+1 and 1+1 can also be achieved by using a PS1000-**.R power module with built-in redundancy. Figure 3 shows 1+1 redundancy using power module with built-in decoupling MOSFET:
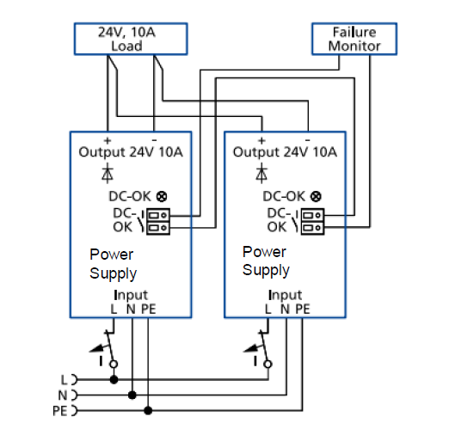
Figure 3 – PS1000-**.R with Internal redundancy in a 10 A load in 1+1 configuration
Figure 4 shows N+1 redundancy using a PS1000-**.R power module with built-in decoupling MOSFET:
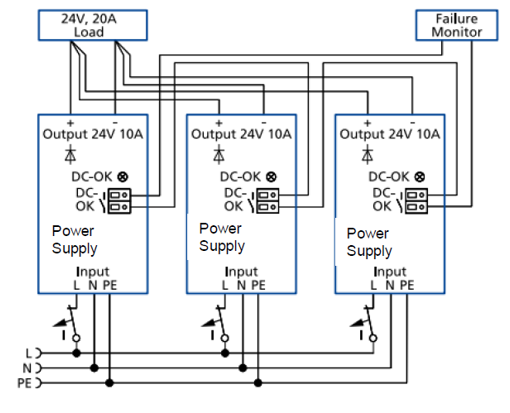
Figure 4 – PS1000-**.R power supply module with internal redundancy in an N+1 configuration with 20 A load
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive regular news and interesting facts from the world of automation.
