Industrial Internet of Things with MQTT and IO-Link Technology
Content of This Article
Industrial Internet of Things with MQTT and IO-Link Technology
There are many ways to achieve the kind of reliable machine-to-machine connectivity that powers the Industrial Internet of Things. Incorporating MQTT devices is one of them. Do you wonder if switching to MQTT-compliant devices could improve your application? Here is what you must know to build an IIoT-ready system.
Why Use MQTT?
Originally created by IBM, MQTT is a lightweight publish-subscribe (“pub/sub”) messaging protocol ideal for use with low-power sensors or large numbers of devices that require cost-effective data exchange and/or cloud connection. This makes it well-suited for IoT applications.
More so than any other protocol supported by Pepperl+Fuchs ICE2 and ICE3 IO-Link masters, MQTT is useful for software development experts who want to build their own solutions using open languages. It is a good option for connecting OT to the cloud or other non-PLC clients but may not be ideal for small-to-medium businesses seeking turnkey solutions from their vendors. Protocols like OPC UA, which the ICE2/ICE3 IO-link masters also support, tend to be better suited for these users.
IO-Link and MQTT
ICE2/ICE3 IO-Link masters from Pepperl+Fuchs are an excellent example of IIoT protocols in action. In addition to letting users work with standards like EtherNet/IP, MODBUS TCP, and PROFINET IO, they also support MQTT and OPC UA. Since these devices are designed for industrial use, they are ideal for linking diverse sensors to create powerful distributed architectures.
Using IO-Link masters with MQTT protocol can make it easier to build IIoT systems. These devices can help companies and organizations streamline mission-critical tasks, such as maintaining IIoT quality of service.
IO-Link masters that support various protocols are especially useful platforms for creating new customized systems. Companies that want to experiment can do so freely without worrying about compatibility. As they build new machine control networks around IO-Link devices, they can add their own custom sensor hardware using a broad range of proven platforms to fine-tune their implementations.
MultiLink™ and MQTT
With MultiLink™ on Pepperl+Fuchs ICE blocks, users gain flexibility when using PLC systems and cloud solutions simultaneously. This translates to an easier and more powerful architecture that provides end-device data to programs that can make informed decisions and perform analytics. OPC UA, MQTT, and MODBUS TCP, all of which are supported by the ICE2/ICE3 IO-Link masters, are common methods for sharing data between systems and/or providing direct control of applications with no strict real-time requirements or, in this example, from end device to SCADA, HMI, or the cloud:
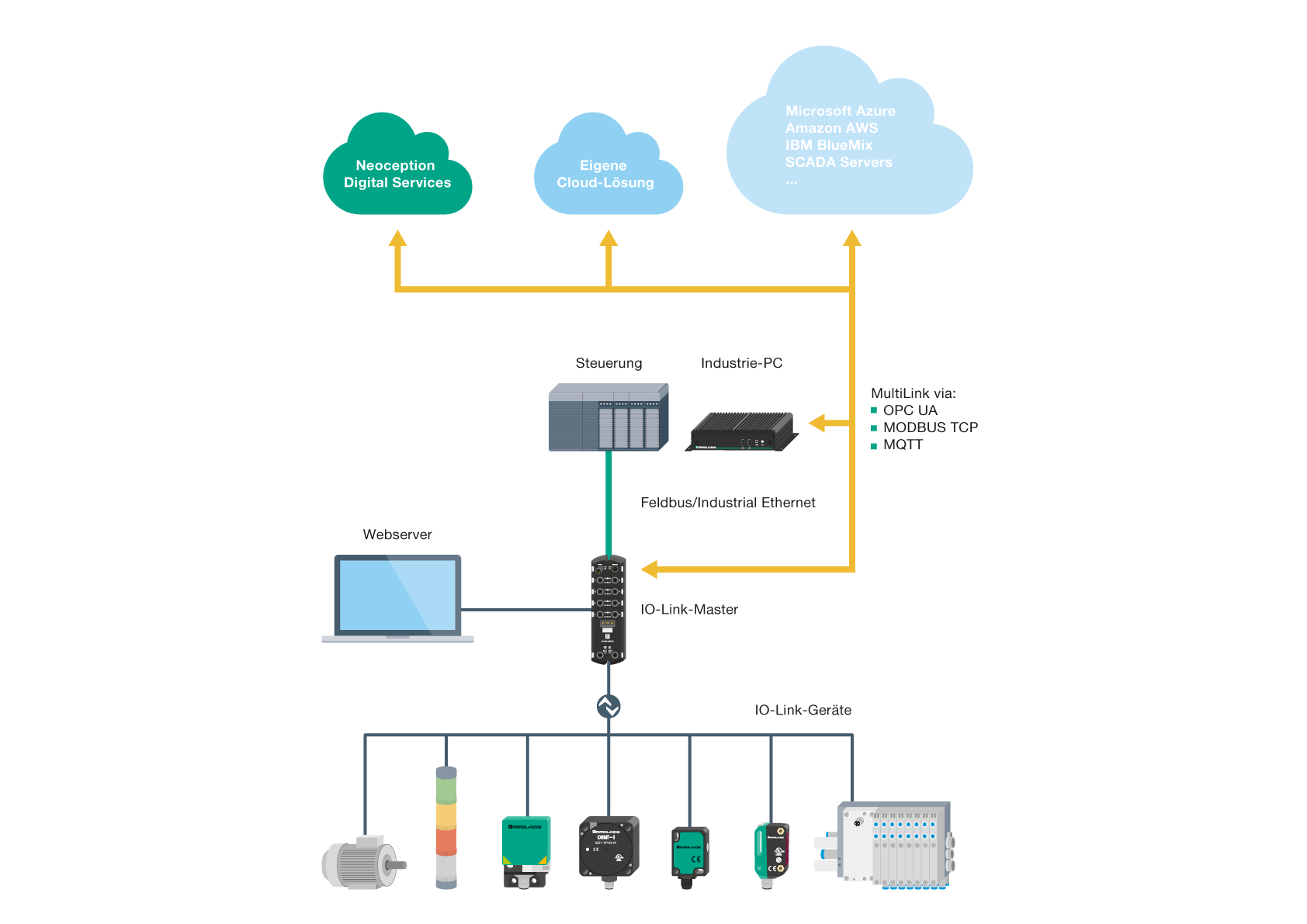
At a Glance:
- EtherNet/IP and PROFINET provide real-time PLC control
- MODBUS TCP can be near real time for PLC, HMI or SCADA
- MQTT and OPC UA provide direct connection to SCADA or cloud
- Users can take advantage of these protocols simultaneously via MultiLink™
- The web-based configuration concept does not require additional software, so it is an optimal solution for standalone applications without PLC control.
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive regular news and interesting facts from the world of automation.
